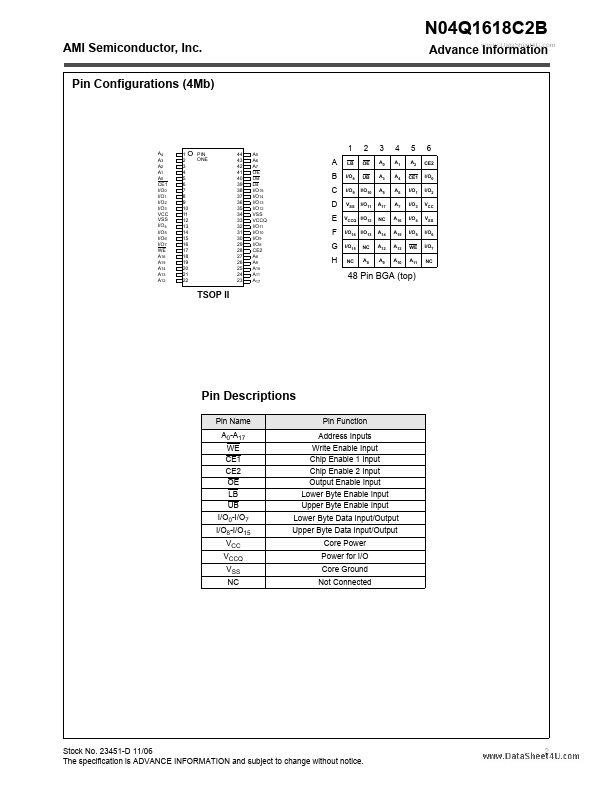
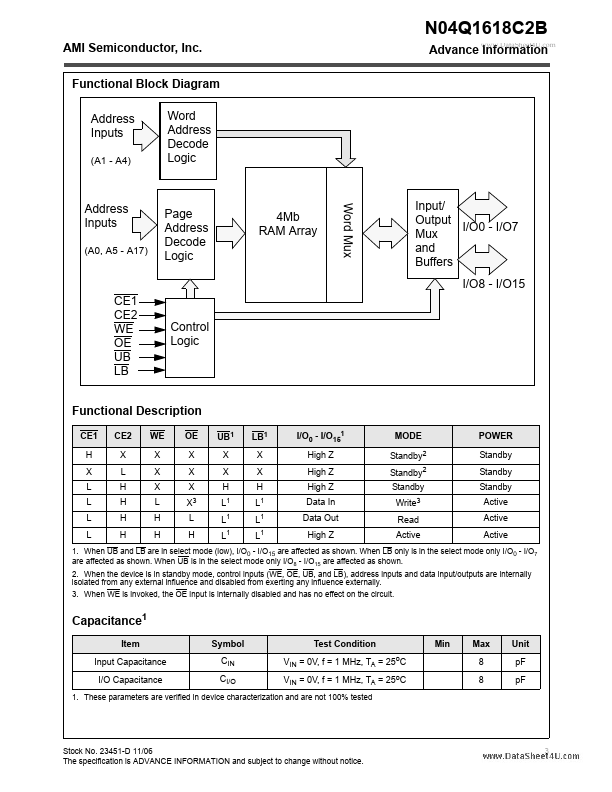
N04Q1618C2B Overview
ULP Memory Solutions 670 North McCarthy Blvd. Suite 220 Milpitas, CA 95035 PH: 408-935-7770 N04Q1618C2B Advance Information.
N04Q1618C2B Key Features
- Multiple Power Supply Ranges 1.1V
- 1.3V 1.65V
- Dual Vcc / VccQ Power Supplies 1.2V Vcc with 3V VccQ 1.8V Vcc with 3V VccQ
- Very low standby current 50nA typical for 1.2V operation
- Very low operating current 400µA typical for 1.2V operation at 1µs
- Very low Page Mode operating current 80µA typical for 1.2V operation at 1µs
- Simple memory control Dual Chip Enables (CE1 and CE2) Byte control for independent byte operation Output Enable (OE) for
- Automatic power down to standby mode
- BGA, TSOP and KGD options
- RoHS pliant